Understanding the Metric System: A Comprehensive Guide
The metric system is a decimal-based system of measurement used internationally. It’s known for its simplicity and uniformity, making it the preferred system in science and many sectors worldwide.
Detailed Description of the Metric System
History and Adoption
- Origin: The metric system originated in France during the late 18th century, a period marked by the quest for rationality and order.
- Adoption: Initially adopted by France, the system gradually gained worldwide acceptance, particularly following the signing of the Metre Convention in 1875. Today, it’s used by almost every country, with the notable exception of the United States, which still primarily uses the customary system.
Units and Categories
- Basic Units: The system is built around three fundamental units: the meter for length, the kilogram for mass, and the second for time.
- Derived Units: From these, various units are derived, such as the newton for force and the joule for energy.
- Prefixes: The system uses a range of prefixes to denote multiples and submultiples, such as “kilo-” for a thousand times (e.g., kilometer) and “milli-” for one-thousandth (e.g., millimeter).
Advantages of the Metric System
- Uniformity: Its decimal-based structure ensures uniformity and ease of understanding.
- Simplicity in Conversion: Converting between units is straightforward, involving only powers of ten.
- Global Standard: Being the international standard, it facilitates global communication and trade.
- Scientific and Technical Use: Its precision and universality make it ideal for scientific and technical fields.
Comparison with Other Systems
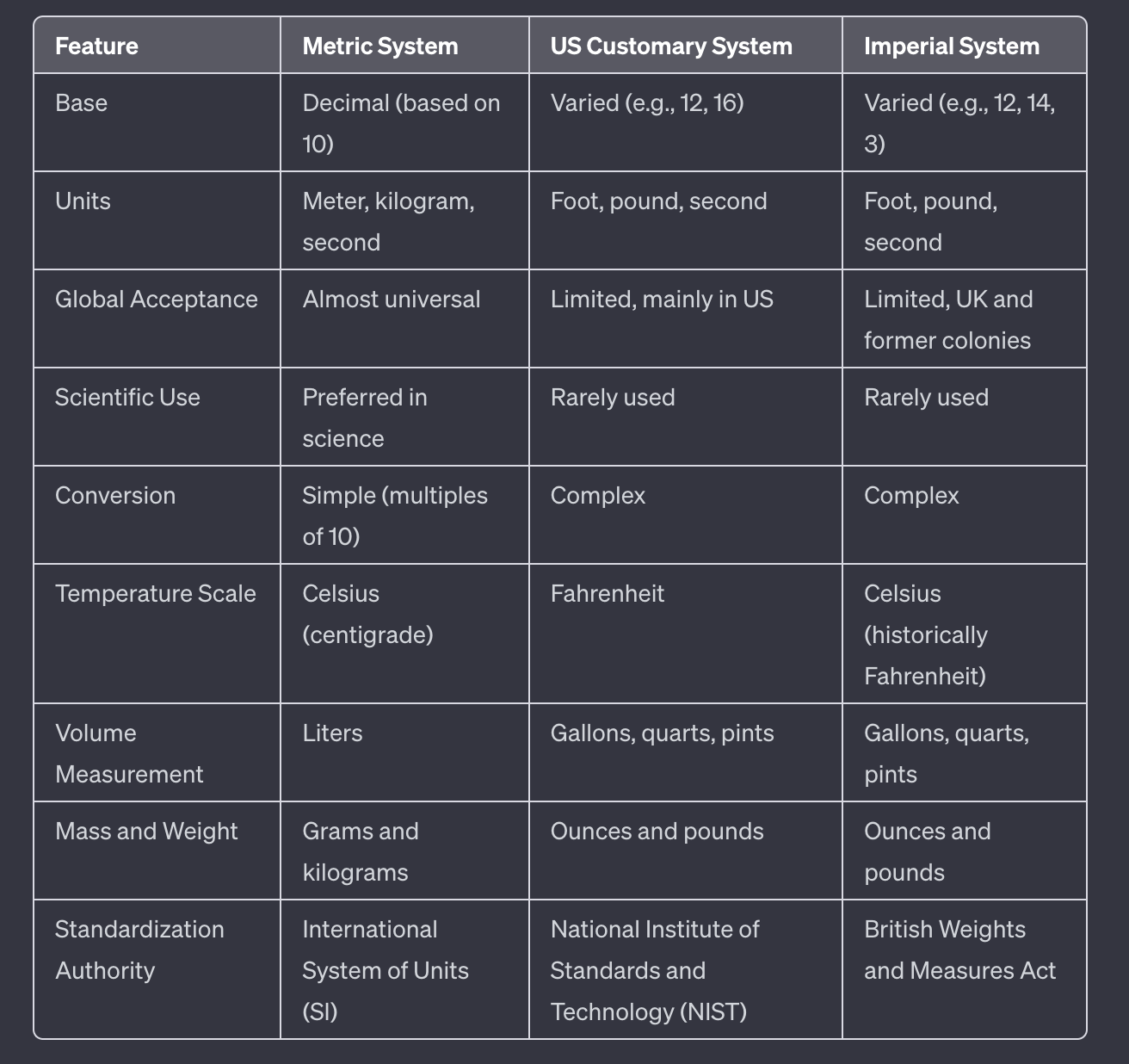
| Feature | Metric System | US Customary System | Imperial System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | Decimal (based on 10) | Varied (e.g., 12, 16) | Varied (e.g., 12, 14, 3) |
| Units | Meter, kilogram, second | Foot, pound, second | Foot, pound, second |
| Global Acceptance | Almost universal | Limited, mainly in US | Limited, UK and former colonies |
| Scientific Use | Preferred in science | Rarely used | Rarely used |
| Conversion | Simple (multiples of 10) | Complex | Complex |
| Temperature Scale | Celsius (centigrade) | Fahrenheit | Celsius (historically Fahrenheit) |
| Volume Measurement | Liters | Gallons, quarts, pints | Gallons, quarts, pints |
| Mass and Weight | Grams and kilograms | Ounces and pounds | Ounces and pounds |
| Standardization Authority | International System of Units (SI) | National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) | British Weights and Measures Act |
Conclusions
The metric system, with its uniformity and ease of use, has become the backbone of international measurement. Its adoption simplifies global communication, trade, and scientific research. The system’s logical structure, built on a decimal base, is a model of efficiency and clarity in measurement, making it an essential tool in a globally interconnected world.
Sources:
https://multiunitconverter.com
https://be1.ru/stat/multiunitconverter.com
https://www.g-idol.com/url.cgi/bbs/?https://multiunitconverter.com
http://www.sitedossier.com/site/multiunitconverter.com
http://mjump.vip2ch.com/https://multiunitconverter.com
https://downforeveryoneorjustme.com/multiunitconverter.com